
Sabine HENNEQUIN



57 rue Cuvier
CP48
75005 Paris
Licence Sciences du Vivant 1st, 2n and 3rd year : Plant biodiversity, morphology, and anatomy.
Master Sciences de l’Univers, Environnement, Ecologie : Plant systematics and ecology, Forest sciences, Phylogeny and evolution, Plant systematics, Tropical diversity
Master in Biology Teaching : Botany
Presentation

Research
I study evolutionary patterns and processes in seed-free plants belonging to the ferns and lycophytes. This involves reconstructing evolutionary relationships between lineages (phylogenies), which can be used to understand morphological evolution, biogeography and adaptation to particular habitats. Whenever available, fossils are used to calibrate these phylogenies, thus providing the time scale for evolutionary events. A second part of my research interests focuses on the assembly of diversity on oceanic islands, in other words, its geographical whereabouts, the role of immigration or speciation and how it is phylogenetically structured.

Mountain rainforest at La Grande Montée, with the tree ferns Cyathea glauca emerging from the canopy
The Mascarene Islands consist of three main islands (La Réunion, Mauritius and Rodrigues) located east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean and part of the South West Indian Ocean hotspot of biodiversity and endemism. Although these oceanic islands share similar geological history, they differ in size, elevation profile, age, distance to the nearest larger land mass (Madagascar) and biodiversity. Ferns are well known for their high dispersal capacity as a result of their reproductive biology, which includes the formation of small meiospores and potentially hermaphrodite gametophytes. Consequently, frequent colonization by ferns from Madagascar and other areas around the Indian Ocean, or even further, is expected, as well as exchange between the Mascarene islands. Indeed, ferns make up an important component of the diverse flora of the Mascarenes, especially in the rain forests, with more than 240 reported species, among which 20% are endemic to these islands. After the Hawaiian Islands, the Mascarenes are the oceanic islands with the highest fern diversity, making them especially suited to study fern evolution in a real-scale Darwinian laboratory. The objectives of this study are multiple : to investigate the patterns of fern diversification in the Mascarene Islands, especially groups undergoing cladogenesis, to identify the processes of island community assembly and to investigate characteristics (such as morphology and life forms) that may be related to better chances of colonization versus speciation.

Erica mountain thicket with Sphagnum (“avoune” type)

Cyathea glauca (Cyatheaceae) or “fanjan femelle”, an emblematic tree fern endemic to La Réunion
This project has been funded by two ATM of the MNHN Paris (2010-2012), the British Council Darwin Now Award (2009), and a Marie Curie Intra-European Fellowship (2008-2010).
This project is currently expanded to the whole South-West Indian Ocean Region, including Madagascar, in collaboration with G. Rouhan. In addition, we are collaborating with a Brazilian team (A. Salino, UFMG Brazil) with a view to comparing how fern diversity is assembled in two geographically distinct areas sharing similar ecology : the Indian Ocean region and the Atlantic Forest in Brazil.
In relation to my project on the ferns from the Mascarene Islands, I am interested in reconstructing the evolutionary relationships in several groups of ferns, especially the genus Ctenitis (Dryopteridaceae) which appears to have radiated in the Indian Ocean region and in the Mascarenes, and the families Thelypteridaceae and Polypodiaceae.
Main coll. : H. Schneider (NHM London), J.-Y. Dubuisson, M. Gaudeul & G. Rouhan (UMR 7205), A. Salino (UFMG, Brazil), A. Ebihara (National Museum of Nature and Science,Tokyo, T. Ranker (U. of Colorado).

(4.) Amauropelta heteroptera (Thelypteridaceae), endemic to La Réunion -
(5.) Grammitis melanoloma (Polypodiaceae), an epiphyte endemic to La Réunion, showing round nude sori and characterized by a black margin -
(6.) Ctenitis crinita (Dryopteridaceae) and sori, endemic to Mauritius. According to our results this genus radiated in the Mascarenes.
This is not to forget my first research interest : the Hymenophyllaceae, or filmy ferns, easily recognized by their very thin leaves (typically one-cell thick) and their marginal sori. During my Ph.D. I studied a genus of the family, Hymenophyllum, which includes approximately 300 species. The phylogeny inferred allowed to propose a new classification for the genus. I was also especially interested in the evolution of morphological characters within the genus, and deciphering its complex biogeographical history is still underway. This requires broadening the taxon sampling of the inferred phylogeny and acquiring nuclear markers. I also draw my attention to the issue of chromosome numbers evolution in the genus, where very variable numbers are reported with n = 11, 12, 13, 14, 18, 21, 22, 26, 28, 36. (coll. J.-Y. Dubuisson, UMR7205 and A. Ebihara, National Museum of Nature and Science, Japan).

Hymenophyllum decurrens (Hymenophyllaceae) from Guadeloupe grows as an epiphyte, as nearly all other Hymenophyllum species

Chromosome number evolution in Hymenophyllum
Another project targeted molecular rate heterogeneity between the two lineages of Hymenophyllaceae : hymenophylloids (= Hymenophyllum) and trichomanoids. We demonstrated that there is a slow-down in the molecular evolutionary rate in the hymenophylloids, and that this phenomenon occurs not only at the chloroplast level, but also seems to take place on the mitochondrion and nuclear levels. With a view to understanding the causes for this deceleration of rate, we investigated the evolutionary history in the family by estimating divergence times and by reconstructing the evolution of the different habitats found in the family (terrestrial, hemiepiphytic and epiphytic). Our results imply that filmy ferns were ancestrally terrestrial and that epiphytism evolved several times independently in the family during the Cretaceous and the Tertiary. Coll. K. Pryer (Duke University) and E. Schuettpelz (U. North Carolina).
Together with J.-Y. Dubuisson, we are further investigating morphological and anatomical evolution in the trichomanoids in relation to habitat. We also aim to propose a biogeographical scenario for the history of the lineage.
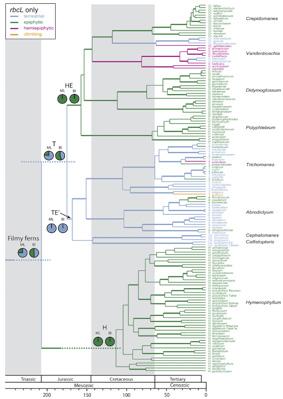
Habitat evolution and divergence times in Hymenophyllaceaem
Fieldwork
Fieldwork is an essential part of my work in order to obtain material of the studied species and to understand their ecological preferences. Collected specimens are preserved as herbarium specimen, contributing to enriching the herbarium collections of the MNHN Paris, and as silica-dried material for DNA-based studies.

Collecting Ctenitis maritima in La Réunion (endemic to the Mascarenes)